One of our most valuable senses, vision, allows us to see the environment around us. The transmission of visual data from the eye to the brain by the optic nerve is crucial to this process. However, cupping of the optic nerve can cause a number of visual problems. We will go further into the world of optic nerve cupping in this complete guide, learning about its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, available treatments, and connection to glaucoma. We will also clarify how low vision services can significantly improve eyesight for folks who are impacted by optic nerve cupping.
Understanding Optic Nerve Cupping
Causes of Optic Nerve Cupping
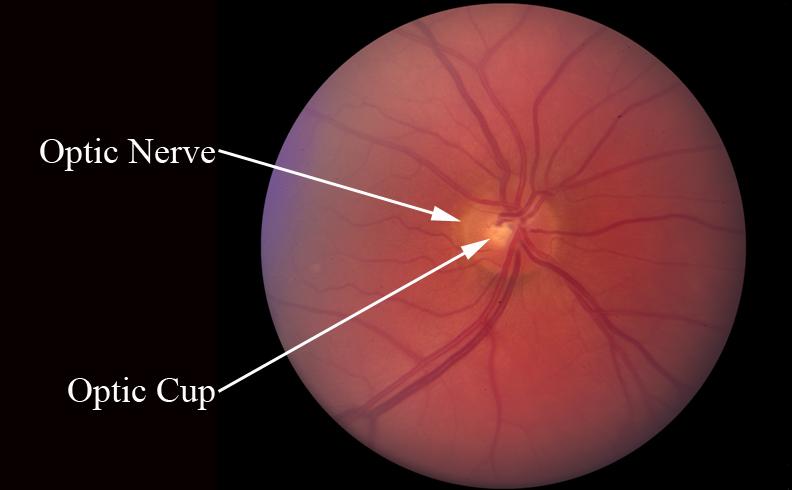
A structural alteration to the optic nerve head is referred to as optic nerve cupping, also known as cupping of the optic nerve. The optic nerve becomes cupped or indented as a result of this alteration, which may impair vision. Elevated intraocular pressure, which over time may harm the optic nerve, is the major cause of optic nerve cupping. This is a defining characteristic of the dangerous eye ailment glaucoma.
Is Optic Nerve Cupping Normal?
Optic nerve cupping is not always an indication of glaucoma, despite the fact that this condition might sometimes be indicated by it. Without getting glaucoma, some people may have a bigger cupping of the optic nerve. This is referred to as “physiologic cupping,” and it is regarded as a typical variation in the structure of the optic nerve. But it’s important to distinguish between physiologic cupping and glaucoma-related cupping.
Optic Nerve Cupping Without Glaucoma
It’s significant to remember that glaucoma isn’t always a factor in situations of optic nerve cupping. Optic nerve cupping may also be influenced by additional factors, such as myopia (nearsightedness) or inherited factors. Even though these conditions might not eventually develop into glaucoma, they nevertheless need to be monitored by an eye care specialist.
The Spectrum of Optic Nerve Cupping
Mild to severe optic nerve cupping is a spectrum condition. Clinical tests and imaging modalities are frequently used to gauge the degree of cupping. For selecting the best course of action and therapy, determining the degree of cupping is essential.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Common Symptoms
Depending on the severity and underlying cause of optic nerve cupping, the symptoms and indicators can change. Typical signs include:
- Patients may notice a gradual shrinking of their visual field due to a loss of peripheral vision.
- vision that is fuzzy or distorted: Straight lines may appear curved or wavy.
- Reduced capacity to perceive in low light circumstances due to difficulty with night vision.
- Frequently changing prescriptions for eyeglasses: Corrective lenses may need to be updated on a regular basis.
Diagnostic Methods and Tools
A thorough eye exam is often required to diagnose optic nerve cupping. Eye care specialists employ a variety of instruments and methods, such as:
- Ophthalmoscopy: A specialist instrument is used to look at the optic nerve head.
- Visual field testing: This determines how much peripheral vision has been lost.
- OCT: A high-resolution imaging technique that offers thorough information on the optic nerve.
- Early identification of optic nerve cupping is crucial because it enables prompt management and intervention.
Treatment and Reversal of Optic Nerve Cupping
Can Cupping of the Optic Nerve Be Reversed?
Optic nerve conditions and the ability to be reversed rely on their underlying etiology and the stage at which it is discovered. Cupping refers to the loss of nerve fibers and is irreversible. Early intervention and efficient management can stop future deterioration and even enhance vision when raised intraocular pressure (as observed in glaucoma) is the cause of optic nerve cupping. Reversing the cupping may be difficult if the optic nerve damage is significant.
Normal Range for Optic Nerve Cupping
The evaluation of optic nerve cupping is crucial for both identifying and tracking changes in eye health. The typical range for optic nerve cupping is determined by eye care professionals using a variety of indicators. Divergences from this range may be a warning of prospective problems.
Low Vision Services and Optic Nerve Cupping
The quality of life for people with optic nerve cupping is significantly improved by low vision services. These services use specific tools and techniques to maximize a person’s remaining vision. For those with optic nerve cupping, low vision aids like magnifiers and electronic devices can considerably increase freedom and everyday duties.
By boosting remaining vision and assisting with everyday duties, low vision devices can greatly raise the quality of life for patients with glaucoma and optic nerve cupping. The kind of low vision equipment a person chooses will depend on their unique requirements and level of visual impairment. Those with glaucoma and/or optic nerve cupping may find the following common low vision aids useful:
Magnifiers:
Portable tools called handheld magnifiers are used to magnify labels, books, newspapers, and other printed objects. They are available in various sizes and magnification levels.
Stand Magnifiers: With their steady magnification and hands-free design, these magnifiers are ideal for lengthy reading sessions. They rest on the reading material.
Electronic video magnifiers (CCTVs): CCTVs show enlarged pictures of books, photographs, or objects on screens and cameras. They frequently offer movable color settings, contrast adjustments, and magnification levels.
Low vision telescopes:
Monocular Telescopes: You may read signs, identify people, or watch TV from a distance using a monocular telescope. They are small, portable, and can be placed on spectacles.
For tasks that require distance vision, such as reading road signs or bus numbers, bioptic telescopes can be flipped down from eyewear.
Materials with Large Print:
For persons with vision loss, large-print books, calendars, and playing cards are easily accessible and can make reading and daily planning easier.
Accessibility software for smartphones and computers:
By magnifying text and reading it aloud, screen magnification software and screen readers can assist users in accessing digital content on computers and smartphones.
Audio Equipment:
Without relying on visual signals, audiobooks, talking watches, and voice-activated assistants like Siri or Alexa can give information and pleasure.
Lighting Fixtures:
People with low vision must have adequate illumination. Brighter, programmable lighting can enhance contrast and lessen glare, making it simpler to read and see items.
Pages holders and reading stands:
The strain on the eyes is decreased since these devices hold books and reading materials at the ideal distance and angle for comfortable reading.
Feeling Markers:
Individuals can recognize and locate everyday objects like buttons, appliances, and household items with the aid of raised tactile markers such as bump dots or tactile labels.
Services for audio description:
With the use of audio description services, those who are blind or visually impaired can follow the plot while viewing television or movies.
Training in Orientation and Mobility:
Individuals with limited vision can learn safe and independent travel practices, including the use of mobility aids like white canes or guide dogs, through orientation and mobility instruction from specialists.
The Link Between Optic Nerve Cupping and Glaucoma
Examining the Relationship
A series of eye conditions known as glaucoma include optic nerve damage and are frequently accompanied by increased intraocular pressure. Glaucoma can be detected by the cupping of the optic nerve, and the two conditions are closely connected. Increased intraocular pressure in glaucoma can cause gradual optic nerve damage and cupping.
Glaucoma-Related Optic Nerve Cupping
Treatment for glaucoma cases with optic nerve cupping generally focuses on controlling intraocular pressure to stop additional damage. In glaucoma patients, medications, laser therapy, and surgery are frequently used to manage intraocular pressure and delay the advancement of optic nerve cupping.
Natural ways to slow optic nerve cupping
Optic nerve cupping or glaucoma cannot be totally prevented or reversed naturally, but certain dietary and lifestyle choices and routines may help limit their growth and preserve general eye health. While speaking with an eye care specialist is necessary for a thorough treatment plan, here are some natural ways to maintain eye health:
Continue to Eat Well:
Include foods high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, especially those that support eye health. Leafy greens, carrots, sweet potatoes, bell peppers, citrus fruits, almonds, and omega-3-rich fish like salmon and mackerel are some of them.
Keep hydrated
All bodily tissues, including those in the eyes, must be properly hydrated to remain healthy. Drink enough water each day to stay well hydrated.
Routine Exercise:
Regular physical activity can enhance blood flow to the optic nerve and assist control intraocular pressure. Be sure to check with your doctor before beginning a new workout regimen.
Control Stress:
Elevated intraocular pressure may be exacerbated by ongoing stress. To lower stress levels, try stress-reduction exercises like yoga, deep breathing, meditation, or mindfulness.
Limit alcohol and caffeine:
Caffeine and alcohol consumption in excess might momentarily raise intraocular pressure. Think about reducing the amount of these things you consume.
Don’t Smoke:
Smoking increases the chance of developing glaucoma and can harm the visual nerve. Smoking cessation can be beneficial for eye health.
Defend Your Eyes Against UV Rays:
When outdoors, put on sunglasses that offer UV protection to lessen the chance of eye damage from ultraviolet radiation.
Keeping a Healthy Weight in Mind
Numerous medical disorders, including glaucoma, are associated with obesity. Intraocular pressure may be controlled by maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and frequent exercise.
Observe the prescription instructions:
Take medications as advised by your doctor if you have been diagnosed with glaucoma or another eye ailment. These drugs can aid in regulating intraocular pressure.
Frequently Scheduled Eye Exams:
Plan routine comprehensive eye exams with a qualified eye care expert. To preserve vision, eye diseases must be promptly identified and treated.
Protect Your Eyes:
Wear the proper eye protection, such as safety goggles or helmets with face shields, when participating in activities that pose a risk of eye injury, such as sports or construction work.
Decrease Screen Time:
To reduce digital eye strain, cut out on extended screen time and take breaks. The 20-20-20 rule states that you should spend at least 20 seconds staring at something 20 feet away every 20 minutes.
Managing diabetes and blood pressure:
Diabetes and high blood pressure can aggravate eye conditions like glaucoma. Manage these problems with medicine, a change in lifestyle, and routine doctor visits.
It’s important to remember that these natural methods are not a replacement for medical care, even though they might improve overall eye health and even halt the advancement of eye diseases. A customized treatment strategy and competent medical attention are necessary for glaucoma and optic nerve cupping. Always seek advice from your eye care professional to choose the best course of action for your unique needs.
Conclusion
The complex eye disease known as optic nerve cupping can significantly impair one’s eyesight. Early detection through routine eye exams is crucial for prompt management and intervention. While some optic nerve conditions can be reversed, others would need continuing care and assistance from low vision agencies. It is essential to comprehend the origins, signs, diagnosis, and available treatments for optic nerve cupping in order to maintain eye health and preserve eyesight.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the term “ocular nerve cupping” mean?
The term “cupping of the optic nerve” refers to a structural alteration that creates an indentation or cup in the optic nerve head. It might indicate glaucoma or another eye issue.
Can cupping of the optic nerve be normal?
Yes, some people may suffer from physiological cupping or their cups are naturally larger from birth.