
Red Eye Medicine
Red eye is one of the most frequently seen complaints in primary care practice and may be an early indicator of serious diseases that require immediate referral. Symptoms of this
Macular degeneration is the primary cause of vision loss in the United States, impacting over 10 million people.
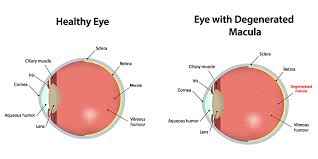
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a kind of eye disease that causes central vision to fade. It occurs when the macula — the region of the eye that regulates crisp, straight-ahead vision — is damaged because of aging. The macula is a component of the retina (the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye).
AMD is a prevalent disorder that is a significant cause of visual loss in elderly people. Although AMD cannot result in total blindness, losing your central vision can make it difficult to see faces, read, or drive.
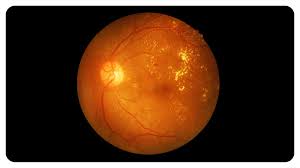
AMD is classified into two types: dry and wet.
The first kind of AMD is dry AMD (also called atrophic AMD). This is the process through which the macula thins with age. Dry AMD manifests itself in three stages: early, moderate, and late.
Wet AMD (also known as advanced neovascular AMD) is a less frequent kind of late AMD that causes more rapid vision loss. It occurs when aberrant blood vessels develop at the rear of the eye, causing damage to the macula.
The symptoms of AMD vary according on the stage.

AMD might be caused by old age or genetics. Other factors, such as smoking, nutrition, or high blood pressure, might be to blame.
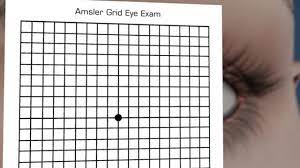
During an eye exam, your eye doctor examines the retina and macula and may use the following tests to detect AMD:
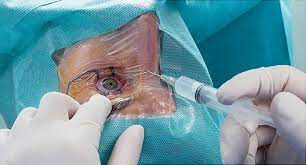
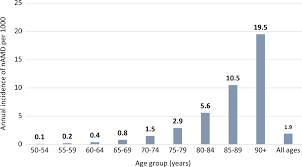
There is no known cure for AMD. Because no one has a complete treatment for macular degeneration, avoid “cures.” It is widely believed that supplements may slow the process of Macular Degeneration. The good news is that food and nutrition may enhance eye health. It’s never too late to start eating a healthy, balanced diet.
Low vision magnifiers and aids give visual solutions for everyday jobs and pastimes as the advancement of Macular Degeneration weakens central vision, causing pictures to lose crisp definition, darken, and blur. There are several low vision gadgets available today, each intended to satisfy the individual’s needs in terms of function and convenience of use.
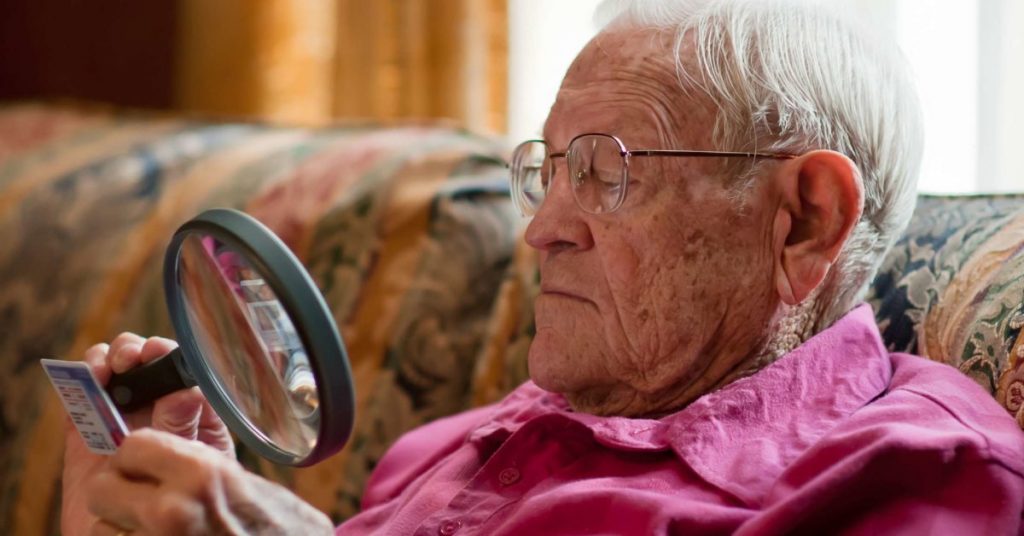

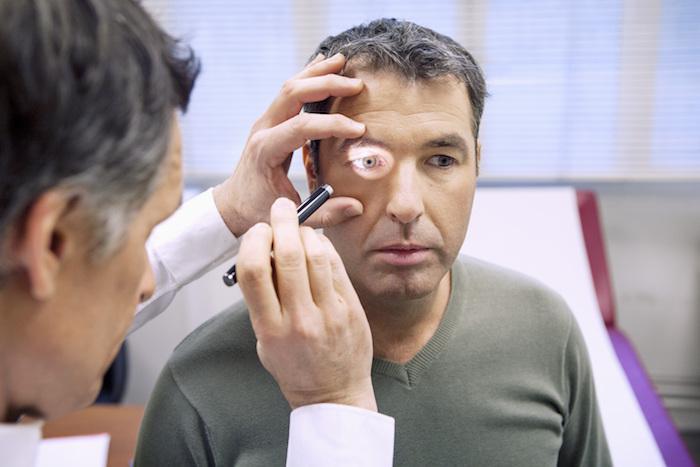
The good news is that visual impairment normally occurs gradually. However, there are two varieties of macular degeneration – ‘wet’ and ‘dry’ – and the ‘wet’ variety causes a rapid loss of central vision, which is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.
Wet Macular Degeneration happens when capillaries underneath the retinal layer bleed, causing retinal cells to die and resulting in blind areas or distorted vision in the central vision.
Low Vision Specialist: They are qualified optometrists or ophthalmologists experienced in the evaluation, treatment, and management of patients with eye diseases that cannot be treated or corrected by medication, surgery, or glasses.
Retinal Doctor: A retina specialist is an ophthalmologist who treats patients with retina disorders and performs office procedures like laser and intraocular injections as well as hospital procedures like vitrectomy.
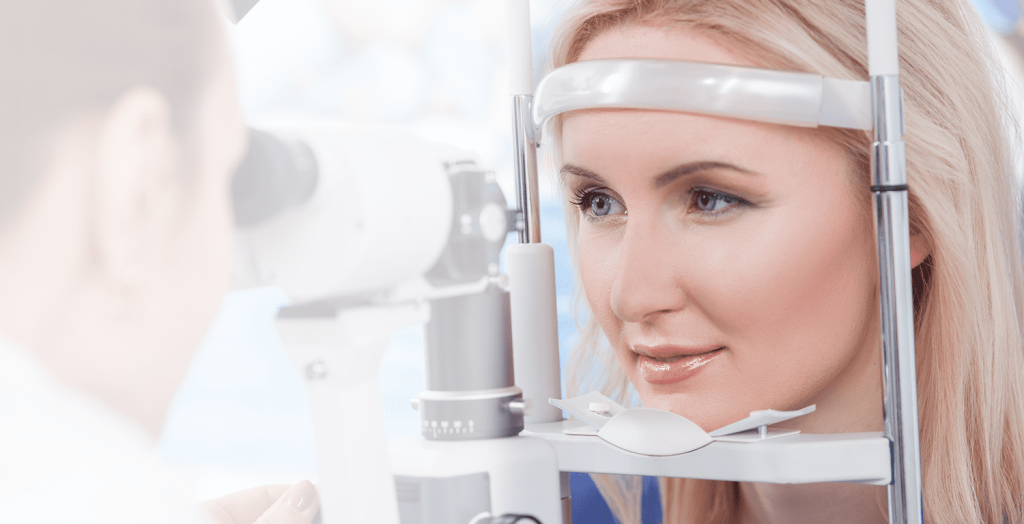

Wet macular degeneration decreases our ability to see shapes, colors, and details. As a consequence, depending on the stage of the disease, you may have:
The Charles Bonnet Syndrome CBS: When you lose a piece of your vision, your brain compensates by creating up images that aren’t real. These visual hallucinations are called the Charles Bonnet syndrome, which is common in macular degeneration.
Not everyone gets AMD or has it in both eyes. However, if you do, living with AMD vision loss may be difficult. Low vision implies that even with glasses, contact lenses, medication, or surgery, your vision loss makes it difficult to do daily duties.
Age-related macular degeneration is the most prevalent cause of significant vision loss in persons aged 50 and above. It is crucial to note that individuals seldom become blind because of it. AMD impairs central vision and, as a result, the ability to discern tiny details.

Visit a low vision specialist to learn more about low vision aids and choose the proper ones. Find one in your region.

Red eye is one of the most frequently seen complaints in primary care practice and may be an early indicator of serious diseases that require immediate referral. Symptoms of this

Hypertension exerts excessive force on blood vessels, ultimately damaging various organs over time – including the eye itself – often manifested by hypertensive retinopathy as the most frequently seen manifestation

Eyes in good health produce aqueous humor continuously and should produce equal amounts for drainage, thus creating an equilibrium in production and drainage in order to maintain stable pressure in

Infants and children can suffer from eye issues just like adults do, so early diagnosis is key in order to prevent permanent damage to their eyesight. Parents need to remain