Your eyes provide an invaluable view into your overall health, with cholesterol deposits being one of the key ways your eye doctor can detect issues in your system.
One of the most frequent symptoms is an arc or ring around the iris known as xanthelasma, typically seen among those under 40 and often indicative of high cholesterol levels in their bodies (familial hyperlipidemia). Although exterior lesions may be harmless, it is still vital to control blood cholesterol levels to keep this from becoming an issue.
Xanthelasma Palpebrarum
This condition is characterized by yellow flat plaques of fatty material in the skin, usually on either upper or lower eyelids and most frequently found near the inner eyelid (medial canthus). Xanthelasma palpebrarum is one of the most prevalent forms of cutaneous xanthoma and occurs both males and females alike; typically painless yet cosmetic issues arise; although eyelid dysfunction rarely results.
Xanthelasmas are benign, fluid-filled lesions composed of fat and cholesterol that often appear around the eyes. Most can range in size from 6mm to over 7cm in diameter, resembling butter beans in appearance. Their causes have been linked with hyperlipidaemia (high cholesterol levels in blood), thyroid dysfunction, inflammatory skin conditions and diabetes mellitus; high levels of cholesterol may trigger enzyme disorders which push fat cells towards the surface.
Treatment of xanthelasma typically focuses on relieving symptoms rather than preventing new ones from appearing, but can include surgical excision, carbon dioxide or argon laser ablation, chemical cauterization electrodesiccation cryotherapy. Blepharoplasty surgery may also be employed in cases with extensive xanthelasma to remove excess skin.
Xanthelasma are typically associated with other illnesses, including diabetes, pancreatitis and alcoholic liver disease; however, they can occur even among healthy individuals; family history suggests they could even be hereditary.
Numerous studies have evaluated atmospheric plasma therapy to treat xanthelasma. One such investigation involved treating 73 patients with bilateral or unilateral xanthelasma using the VAD technique offered by Europe Medical s.r.l. of Montesilvano Italy using photos before and after VAD treatments by an independent observer for 11-years after having received atmospheric plasma treatments from Europe Medical Srl in Montesilvano Italy; results demonstrated it is an effective, non-invasive means to reduce xanthelasma; low recurrence rates were observed while treatment was well tolerated; significant improvement could be seen immediately post treatment as early as one treatment session!
Corneal Arcus
Cholesterol build-up in the eye can form yellowish fatty deposits known as xanthelasma that indicate too high of a cholesterol intake, according to Cleveland Clinic. These deposits typically appear around the eyes but they can also appear in palms of hands and lower legs – another indicator that your levels have reached dangerously high levels.
One sure sign of high cholesterol levels is corneal arcus – a grayish white ring located at the periphery of the cornea and usually seen among individuals over 50 years of age. This ring can be associated with dyslipidemia – a major risk factor for coronary heart disease.
Arcus may appear in either eye and is most prominent around 12 o’clock on either eye’s cornea. More likely to affect women than men and increasing with age, its presence serves as an early warning system of familial hypercholesterolemia – an illness in which cholesterol levels become abnormally high – also known as Arcus Senilis.
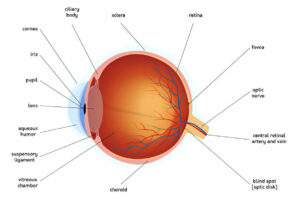
This condition is caused by the accumulation of cholesterol in blood vessel walls supplying retina. Once these lipids accumulate, they can restrict blood flow leading to atherosclerosis – an illness which has the potential to lead to heart attack, stroke, kidney disease or even death.
Your eye doctor can measure its thickness and look for other signs of hypercholesterolemia, including thickening of corneal epithelial cells, formation of cataract or glaucoma and family history of coronary heart disease if the corneal arcus occurs in people under 40; such cases indicate familial hypercholesterolemia. Furthermore, using it as a screening tool against atherosclerosis in Caucasian patients – its sensitivity and specificity being 19% and 100% respectively with 55% negative predictive value suggests it might also detect multivessel coronary artery disease cases in these individuals under 40.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a condition caused by high blood sugar levels that damages the retina, the thin membrane that lines the back of our eyes and captures light to send electrical impulses directly to our brains in order to create visual images. Over time, high blood sugar levels can weaken blood vessel walls within our retina, leading them to leak or bleed and reduce vision dramatically. DR affects approximately four million Americans annually.
Poorly constructed blood vessels can easily burst, damaging retinal tissues. As damage worsens, fragile new blood vessels may form that will bleed or burst under pressure causing even greater eye damage and eventually blindness.
Diabetic Retinopathy causes symptoms that include blurry or distorted vision and difficulty reading or seeing items at distances. It is the leading cause of adult blindness.
As part of your diabetic retinopathy treatment plan, regular eye exams with an eye doctor are the key to protecting your vision from diabetic retinopathy. They use special equipment to examine your eyes for swelling blood vessels, leaky fluid sacs and changes to pupil size as well as any areas with missing or blurred vision that need assessment.
retinopathy in its early stages does not require treatment; however, you should work to control diabetes by keeping blood sugar, pressure and cholesterol within healthy range.
If you have diabetes, it is essential that you visit your physician regularly for eye exams and discuss blood sugar management with him or her. Furthermore, you should avoid smoking and address other risk factors for diabetes like high blood pressure, cholesterol levels and obesity. In more advanced cases of retinopathy laser surgery or injections may be needed in order to slow further vision loss or recover existing vision issues; furthermore this reduces the likelihood that vitrectomy surgery – the procedure in which blood is removed from an eye – might become necessary.
Dry Eye
High cholesterol levels are known to put individuals at an increased risk for heart disease, but they also affect eyes. High cholesterol can contribute to dry eye syndrome – which involves an insufficient supply of tears to lubricate the eye and protect it from irritation – as it’s a common eye condition which may range from mildly irritating to severely disabling.
People with a family history of high cholesterol are at an increased risk for dry eye. Furthermore, several medications such as antidepressants, blood pressure medication and hormone therapy used to treat menopause have also been linked with dry eye. Furthermore, environmental factors like windy or smoky environments as well as prolonged use of screens can cause the tear film to evaporate faster than it should. It’s more prevalent among women as well as as people age; but anyone may experience it.
Treatment options for symptomatic dry eye vary, with most treatments focused on soothing and lubricating the surface of the eyes to promote proper functioning. Over-the-counter artificial tears or eye ointments may help with mild symptoms; while incorporating blinking several times per minute into daily routine or wearing wraparound sunglasses to protect from sun glare may aid those experiencing more severe issues.
The National Eye Institute (NEI) is exploring methods of improving treatment for Dry Eye Syndrome (DES), such as developing topical corneal nerve stimulators to increase eye nerves’ sense of when tears have evaporated. Researchers have also focused on increasing the body’s natural production of an oily substance that forms most of a natural tear film. Recent research on rats revealed that using recombinant human lubricin multiple times per day significantly reduced dry eye symptoms and enhanced the quality of the ocular surface, even when used multiple times daily. Researchers also observed that this ointment reduced inflammation and promoted healing on the eye’s surface, with hopes that eventually, recombinant human lubricin could become an alternative treatment modality instead of current solutions which often are ineffective or cause side effects.